One of the key treatment strategies for managing diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes, is insulin therapy. One such insulin therapy is the use of insulin lispro, a rapid-acting insulin analog. In this guide, we’ll dive deeper into the concept of an insulin lispro sliding scale, which is a method of adjusting the dose of insulin based on the individual’s blood glucose levels.

What is Insulin Lispro?
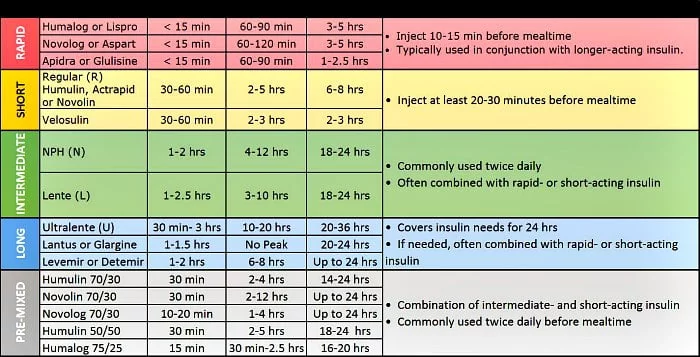
Insulin lispro is a rapid-acting human insulin analog that works quicker and lasts for a shorter duration than regular human insulin. It begins to work 15 minutes after injection, has its maximum effect between 30 and 90 minutes, and lasts for around 3-5 hours.
What is a Sliding Scale Insulin Regimen?
A sliding scale insulin regimen adjusts the dose of insulin in response to the patient’s blood sugar levels. The higher the blood glucose level, the more insulin is administered. This method is often used in hospitalized patients or those unable to eat a consistent amount of carbohydrates at each meal.
The Insulin Lispro Sliding Scale
The insulin lispro sliding scale is customized to each individual’s needs, based on their blood sugar readings. The physician usually sets a target blood glucose range and the patient adjusts their insulin dosage accordingly. A common sliding scale could look something like this:
| Blood Glucose Level (mg/dL) | Insulin Lispro Dose (units) |
|---|---|
| <70 | Contact healthcare provider |
| 70-150 | 0 |
| 151-200 | 2 |
| 201-250 | 4 |
| 251-300 | 6 |
| 301-350 | 8 |
| 351-400 | 10 |
| >400 | Contact healthcare provider |
Note: This is a generic chart, and the actual insulin doses may differ based on individual needs. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Important Considerations
- The sliding scale approach relies heavily on frequent blood glucose monitoring. It’s crucial to understand how to correctly measure your blood sugar levels.
- It doesn’t take into account the carbohydrates in meals, which can greatly influence blood sugar levels. For this reason, the sliding scale method is often used in combination with other insulin dosage methods.
- Regular consultation with your healthcare provider is essential when using the insulin lispro sliding scale. You’ll need to report any significant changes in blood glucose levels, as this could indicate a need for dosage adjustments.
- Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and a healthy lifestyle are all crucial components of successful diabetes management. The insulin lispro sliding scale should be part of a comprehensive diabetes care plan.
In conclusion, the insulin lispro sliding scale can be an effective tool for adjusting insulin doses and managing blood glucose levels in individuals with diabetes. However, it should be used under the close supervision of a healthcare provider and in combination with other strategies for comprehensive diabetes management.
FAQ
Yes, lispro, a rapid-acting insulin, can be administered using a sliding scale. This method adjusts the dose based on the individual’s current blood glucose level, allowing for more precise control of blood sugar.
Insulin per sliding scale is a method where the dose of insulin administered is adjusted based on the patient’s current blood glucose reading. The scale provides guidelines on how many units of insulin to administer, increasing or decreasing the dose in response to the blood sugar level.
The amount of lispro insulin taken varies depending on the individual’s insulin sensitivity, carbohydrate intake, and blood glucose level. Doses are tailored to the individual’s needs and are determined based on patterns of blood glucose readings and the advice of a healthcare provider.
The effect of 10 units of insulin on blood sugar can vary widely among individuals. Generally, one unit of rapid-acting insulin (like lispro) can lower blood sugar by about 30-50 mg/dL, but this can differ based on individual insulin sensitivity, body weight, and other factors. It’s essential to monitor blood glucose levels and consult with a healthcare provider to understand how insulin affects you personally.
The amount of insulin needed for a blood sugar level of 300 mg/dL depends on the individual’s insulin sensitivity and the prescribed sliding scale. For example, based on a common sliding scale, one might take 6-10 units of rapid-acting insulin for blood sugar in this range, but this should be personalized and confirmed with a healthcare provider.
The insulin dose for a blood sugar level of 250 mg/dL will depend on the individual’s specific sliding scale protocol. For instance, on a typical sliding scale, 4-6 units of rapid-acting insulin might be recommended for this blood sugar level, but the exact dose should be determined by a healthcare professional based on the patient’s individual needs and medical advice.
References:
- American Diabetes Association. (2022). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes – 2022. Diabetes Care, 45(Supplement 1), S1-S238. Retrieved from https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/45/Supplement_1
- Davies, M., Storms, F., Shutler, S., Bianchi-Biscay, M., & Gomis, R. (2005). Improvement of glycemic control in subjects with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes: comparison of two treatment algorithms using insulin glargine. Diabetes care, 28(6), 1282-1288. Retrieved from https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/28/6/1282
- Mayo Clinic. (2022). Insulin and weight gain: Keep the pounds off. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/in-depth/insulin-and-weight-gain/art-20047836
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2020). Insulin, Medicines, & Other Diabetes Treatments. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/insulin-medicines-treatments
- Wolpert, H. A., & Atakov-Castillo, A. (2013). The dawn of a new era in basal insulin therapy. Diabetes Care, 36 Suppl 2(Suppl 2), S253-9. Retrieved from https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/36/Supplement_2/S253