Insulin resistance symptoms can be hard to spot at first. But knowing them is key to staying healthy. When your body doesn’t respond well to insulin, it can cause many health problems. It’s important to understand these symptoms to manage your metabolic health.
Anyone can get insulin resistance, no matter their age or background. Knowing the signs helps prevent bigger health issues. Spotting these symptoms is the first step to a healthier life.
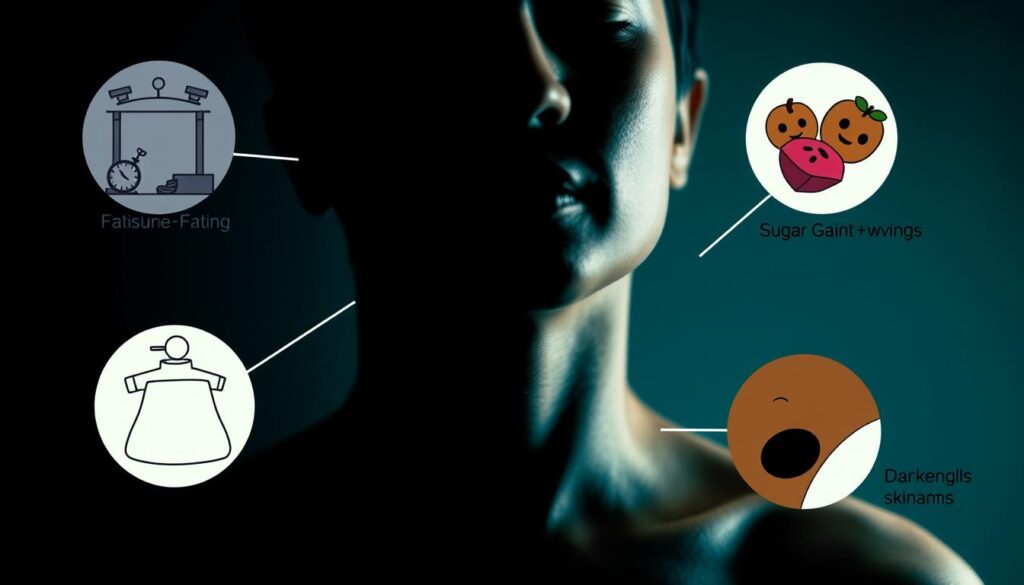

A close-up view of a human silhouette surrounded by visual representations of insulin resistance symptoms, such as fatigue illustrated with dim lighting, weight gain depicted with subtle scales, sugar cravings shown with sweet treats, and darkened skin patches around the neck and underarms as shadowy areas. Emphasize a sense of imbalance and health struggle through color contrasts and abstract shapes.
Managing insulin resistance symptoms is possible with the right steps. Making smart diet and lifestyle choices can lower your risk. Keep reading to learn more about these symptoms and how to improve your metabolic health.
Understanding Insulin Resistance and Its Impact on Health
Insulin resistance happens when the body’s cells don’t respond well to insulin. This hormone helps control blood sugar levels. Knowing the signs of insulin resistance is key to avoiding serious health problems. Factors like genetics, environment, and lifestyle play a role in causing it.

When cells resist insulin, the pancreas makes more insulin. This leads to high insulin levels in the blood. This can harm your health, raising the risk of type 2 diabetes and other issues.
A visual representation of insulin resistance symptoms, featuring a close-up of skin exhibiting dark patches, illustrating acanthosis nigricans, alongside an abstract depiction of insulin molecules, with an overlay of symbols representing fatigue, cravings for sugar, and increased thirst, all set against a soft gradient background to convey a sense of health and awareness.
Insulin resistance is linked to diabetes. It’s a step before type 2 diabetes. Spotting the signs of insulin resistance early can stop diabetes. Knowing the causes of insulin resistance and acting early can lower your risk.
What Is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance means the body’s cells don’t react well to insulin. This can cause high blood sugar levels. It increases the chance of getting type 2 diabetes and other health issues.
How Insulin Resistance Affects Your Body
Insulin resistance can harm your health a lot. It raises the risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other problems. Knowing the signs of insulin resistance and its causes helps you take steps to manage it.
The Relationship Between Insulin Resistance and Diabetes
The link between insulin resistance and diabetes is complex. Insulin resistance leads to type 2 diabetes. Spotting the signs of insulin resistance early can prevent diabetes. Understanding the causes of insulin resistance and acting early can lower your risk.
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Insulin Resistance | A condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin |
| Type 2 Diabetes | A disease characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance |
How Do You Know If You’re Insulin Resistant? Key Physical Signs
Diagnosing insulin resistance involves looking for certain physical signs. These signs can be small but show that the body struggles with blood sugar control. Common signs include weight gain around the midsection, feeling tired, and having skin tags.
Other signs might include:
- Acne or other skin problems
- Darkening of the skin on the neck, armpits, or groin
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
These signs often mean the body is making too much insulin. This is because it tries to keep blood sugar levels stable. Recognizing these signs and getting medical advice is the first step to managing insulin resistance.

A close-up illustration of a person’s arm showing signs of insulin resistance, featuring skin changes like acanthosis nigricans, alongside visual elements representing high insulin levels, such as glucose molecules and warning signs. The background is soft and medical-themed, emphasizing a clinical setting.
It’s important to remember that these signs can also mean other health issues. So, it’s key to talk to a doctor to find out the real cause. With a doctor’s help, you can create a plan to manage your insulin resistance and lower your risk of other health problems.
Common Risk Factors and Lifestyle Indicators
Insulin resistance is a complex condition. It’s influenced by genetics, environment, and lifestyle. Knowing the risk factors for insulin resistance helps in preventing and managing it. Lifestyle choices, like diet and exercise, are key in determining risk.
Several lifestyle indicators can raise the risk of insulin resistance. These include a diet rich in saturated fats and sugars, not enough exercise, and gaining too much weight. Some people are more at risk due to their genes. By understanding these factors and making smart lifestyle choices, people can lower their risk of insulin resistance and related health issues.
- Dietary habits: Eating a lot of processed foods and added sugars can increase the risk of insulin resistance.
- Physical activity patterns: Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and lower the risk of insulin resistance.
- Genetic and environmental factors: Certain genetic predispositions and environmental factors, like exposure to pollutants, can also contribute to insulin resistance.
By knowing these risk factors for insulin resistance and lifestyle indicators, people can take steps to reduce their risk. This helps in maintaining good metabolic health.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Dietary habits | Consuming a diet high in processed foods and added sugars |
| Physical activity patterns | Lack of regular physical activity |
| Genetic and environmental factors | Certain genetic predispositions and environmental factors, such as exposure to pollutants |
Medical Tests and Diagnostic Criteria
Diagnosing insulin resistance requires several medical tests and evaluations. Doctors use different criteria to find out if you have it and how severe it is.
Blood Tests and Measurements
Blood tests are key in diagnosing insulin resistance. They check your blood for glucose, insulin, and other important markers. Tests like fasting glucose, oral glucose tolerance, and insulin sensitivity tests are common.
Working With Healthcare Providers
It’s important to work closely with your healthcare providers. They will help understand your test results, create a plan for you, and guide you on lifestyle changes and treatments.
Understanding Your Test Results
It’s vital to understand your test results to manage insulin resistance. Your healthcare providers will explain the results, talk about what they mean, and help you improve your insulin sensitivity and health.
By following these steps and working with healthcare providers, you can manage your metabolic health. This can help reduce the risk of related conditions.
| Test | Description |
|---|---|
| Fasting Glucose Test | Measures glucose levels after an overnight fast |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test | Measures glucose levels after consuming a sugary drink |
| Insulin Sensitivity Test | Measures the body’s ability to use insulin effectively |
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Metabolic Health
Understanding and managing insulin resistance is empowering. Recognizing signs and symptoms is the first step. Then, take action to tackle the root causes.
Start with lifestyle changes like eating well and staying active. Work with your doctor to track your progress. Your metabolic health is key to your overall well-being.
Use your knowledge to take control of your health. By managing insulin resistance, you can live a full and energetic life. Your journey to better health starts today.
FAQ
What is insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance happens when your body’s cells don’t respond well to insulin. Insulin helps control blood sugar levels. This condition can cause blood sugar to rise and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
What are the signs and symptoms of insulin resistance?
Signs of insulin resistance include gaining weight, feeling tired, and having skin tags. You might also notice dark, velvety skin patches and polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) in women.
How does insulin resistance affect my health?
Insulin resistance can harm your health a lot. It’s a big risk factor for type 2 diabetes and heart disease. It also raises the risk of fatty liver disease and some cancers.
What factors contribute to insulin resistance?
Poor diet, not moving enough, and genetics can lead to insulin resistance. Stress and toxins in the environment also play a part.
How can I be diagnosed with insulin resistance?
Doctors use blood tests to check glucose and insulin levels to diagnose insulin resistance. They also look at waist size and body mass index (BMI). Oral glucose tolerance tests help measure how well your body uses insulin.
What can I do to manage insulin resistance?
To manage insulin resistance, start with healthy habits. Eat well, exercise more, and handle stress. Sometimes, doctors will prescribe medicine to control blood sugar.
Refrences
- American Diabetes Association. (2023). Diagnosing and managing insulin resistance. Retrieved from https://diabetes.org/health-wellness/insulin-resistance
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023). What is insulin resistance? Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/about/insulin-resistance-type-2-diabetes.html
- Diabetes UK. (2023). Understanding insulin resistance and its role in diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.diabetes.org.uk/insulin-resistance
- Kahn, S. E., Hull, R. L., & Utzschneider, K. M. (2006). Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature, 444(7121), 840–846. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05482
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2023). Insulin resistance and prediabetes. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/prediabetes-insulin-resistance
- Roden, M., & Shulman, G. I. (2019). The integrative biology of type 2 diabetes. Nature, 576(7785), 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1797-8
- Stern, J. H., Rutkowski, J. M., & Scherer, P. E. (2016). Adiponectin, leptin, and fatty acids in the maintenance of metabolic homeostasis through adipose tissue crosstalk. Cell Metabolism, 23(5), 770–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.04.011
- World Health Organization. (2023). Diabetes: Key facts and figures. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes