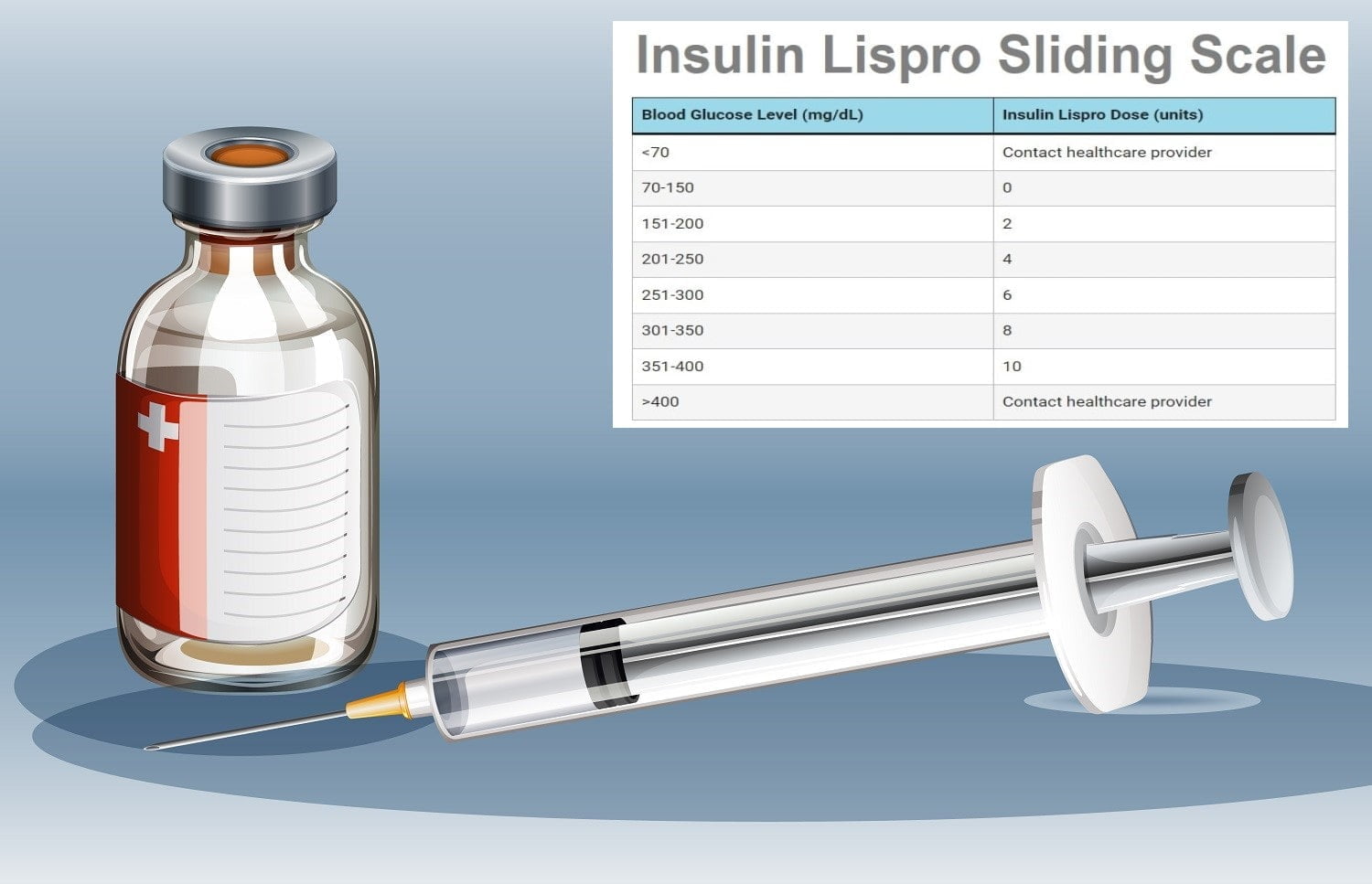
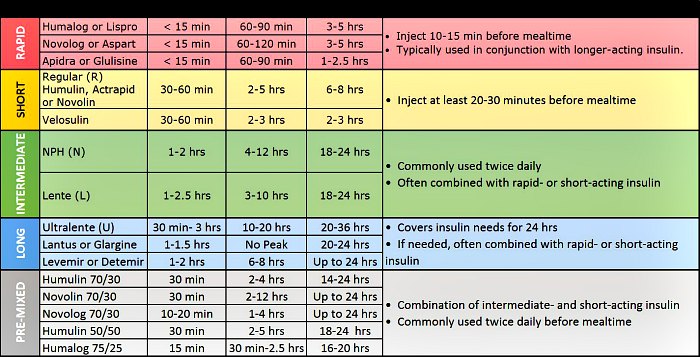
Is glucagon a hormone or enzyme? Glucagon is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a vital role in regulating glucose levels in the body. It is often referred to as a hormone enzyme, which means it acts both as a hormone and an enzyme.
Table of Contents
In this article, we’ll delve into what glucagon is, its functions, and why it is so important to our overall health and well-being.
What is Glucagon?
Glucagon is a hormone that is produced and secreted by alpha cells in the pancreas. It is made up of 29 amino acids and is structurally similar to other hormones, such as insulin and growth hormone.
What cells release glucagon? When glucagon is released into the bloodstream, it acts on target cells, such as liver cells, to stimulate the production of glucose. This glucose is then released into the bloodstream, where it can be used by the body’s cells for energy. 01
The Role of Glucagon in Glucose Metabolism
Glucagon plays a crucial role in regulating glucose levels in the body. When glucose levels in the bloodstream are low, such as during fasting or intense physical activity, the pancreas releases glucagon. This hormone stimulates the liver to break down stored glycogen into glucose, which is then released into the bloodstream.
This increase in glucose levels helps to maintain normal blood sugar levels and provides the body with the energy it needs. Conversely, when glucose levels in the bloodstream are high, such as after a meal, insulin is released by the pancreas. Insulin acts to lower glucose levels in the bloodstream by promoting the uptake and storage of glucose by the body’s cells.
How Glucagon Affects Weight Management
In addition to regulating glucose levels, glucagon also plays a role in weight management. When glucose levels in the bloodstream are low, glucagon stimulates the liver to break down stored glycogen into glucose, as mentioned earlier. This process also releases fatty acids into the bloodstream, which can then be used by the body’s cells for energy.
This release of fatty acids helps to prevent the breakdown of muscle tissue for energy, which can occur during periods of low glucose levels. Additionally, the release of fatty acids can also stimulate the burning of fat for energy, making glucagon an important hormone in weight management.
The Relationship Between Glucagon and Insulin
Glucagon and insulin work in a delicate balance to regulate glucose levels in the body. When glucose levels are high, insulin is released to lower them. Conversely, when glucose levels are low, glucagon is released to increase them.
This interplay between insulin and glucagon helps to maintain normal blood sugar levels, providing the body with the energy it needs while also preventing excessive glucose levels that could lead to health problems such as diabetes.
Glucagon and Health Conditions
While glucagon is an important hormone in regulating glucose levels, imbalances in its production and secretion can lead to various health conditions. For example, conditions such as type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes can result in a lack of glucagon production and secretion, leading to hypoglycemia or low blood sugar levels.
In addition, excessive secretion of glucagon can also lead to elevated glucose levels and contribute to the development of conditions such as insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Where is glucagon stored:
Glucagon is stored in secretory granules within the alpha cells of the pancreas. These granules contain high concentrations of glucagon, ready to be released into the bloodstream when needed. When glucose levels in the bloodstream drop, the alpha cells are triggered to release glucagon into the bloodstream, which can then stimulate the liver to break down stored glycogen into glucose, which is then released into the bloodstream to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
What is the effect of glucagon:
The primary effect of glucagon is to raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to break down stored glycogen into glucose, which is then released into the bloodstream. This helps to maintain normal blood sugar levels, especially when glucose levels are low.
In addition to its role in regulating glucose levels, glucagon also has several other important functions in the body. For example, it stimulates the breakdown of fats in adipose tissue, which releases fatty acids into the bloodstream to be used as energy. It also stimulates the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, such as amino acids and lactate.
Glucagon also plays a role in regulating insulin sensitivity and can help to prevent insulin resistance. This is important in preventing the development of type 2 diabetes and other health conditions related to insulin imbalances.
Overall, the effects of glucagon are crucial in maintaining overall health and preventing the development of certain health problems. It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and seek medical advice when necessary to regulate glucagon levels and prevent imbalances that could lead to health problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, glucagon is a vital hormone enzyme that plays an important role in regulating glucose levels in the body. It works in a delicate balance with insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels and is also involved in weight management. Understanding the role of glucagon in our bodies and its functions is crucial in maintaining overall health and preventing the development of certain health conditions.
It is important to note that maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, can help to regulate glucagon levels and prevent imbalances that could lead to health problems. Regular monitoring of glucose levels and seeking medical advice when necessary are also important in maintaining optimal health.
FAQs
Q1. What is glucagon made of?
Glucagon is made up of 29 amino acids.
Q2. What cells in the pancreas produce glucagon?
Glucagon is produced and secreted by alpha cells in the pancreas.
Q3. How does glucagon affect glucose levels in the body?
When glucose levels in the bloodstream are low, glucagon stimulates the liver to break down stored glycogen into glucose, which is then released into the bloodstream. This helps to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
Q3. What is the relationship between glucagon and insulin?
Glucagon and insulin work in a delicate balance to regulate glucose levels in the body. When glucose levels are high, insulin is released to lower them and when they are low, glucagon is released to increase them.
Q4. Can imbalances in glucagon levels lead to health problems?
Yes, imbalances in glucagon production and secretion can lead to various health problems, such as hypoglycemia, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and seek medical advice when necessary to regulate glucagon levels and prevent health problems.